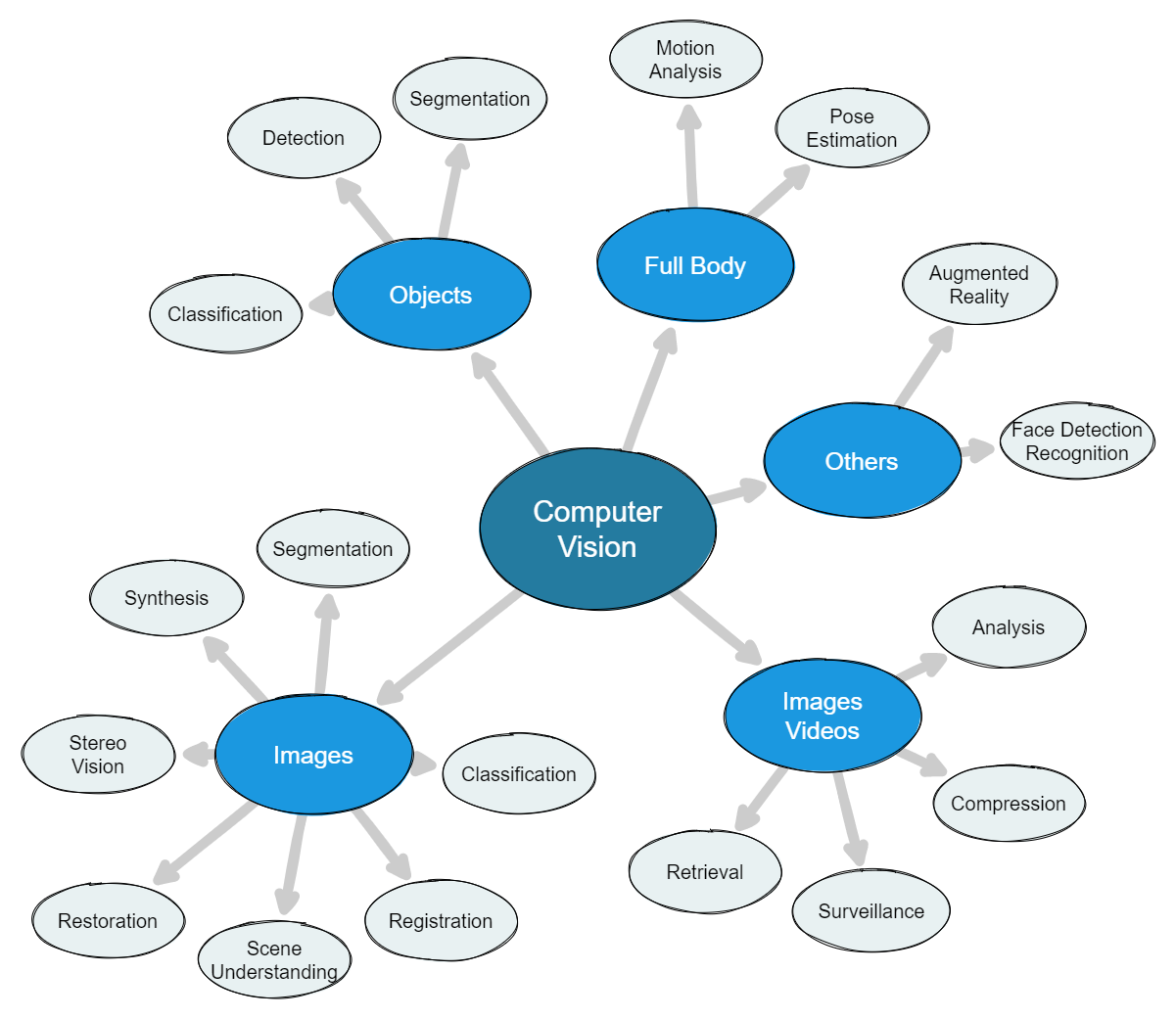
Computer Vision Problems
- Image Classification: categorizes an image into one of several predefined classes based on its features and characteristics.
- Object Detection: identifies and locates objects in an image or video.
- Object Segmentation: separates an object from the background in an image.
- Image Restoration: restore a degraded or damaged image to its original form.
- Face Detection and Recognition: detects and recognizes human faces in images and videos.
- Image Registration: aligns two or more images to a common reference frame.
- Stereo Vision: estimates the depth of objects in an image based on the differences in the images captured by two cameras.
- Motion Analysis: detects and tracks moving objects in a video sequence.
- Image Segmentation: divides an image into multiple segments, each corresponding to a different object or region.
- Scene Understanding: analyzes and interprets the contents of an image or video to understand the relationships between objects and their contexts.
- Pose Estimation: determines the position and orientation of objects in an image or video.
- Image and Video Compression: reduces the size of images and videos while preserving their quality.
Image Synthesis: generates new images based on existing photos or data.
- Image and Video Retrieval: searches and retrieves images and videos based on their content and metadata.
- Image and Video Surveillance: detects and tracks objects and events in real-time using cameras and other sensors.
- Image and Video Analysis: extract information and insights from images and videos, such as image classification, object detection, and scene understanding.
- Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality: applications that use computer vision to enhance or replace the real-world view with digital content.