What is Deep Learning?
What is Deep Learning?
Deep Learning, or DL for short, is a subfield of machine learning that uses multi-layered artificial neural networks to model and solve complex problems. It is inspired by the structure and function of the human brain, and its goal is to simulate the neural processes that enable human perception, thought, and decision-making.
“In short, deep learning is a subset of methods in the machine learning toolbox, primarily using artificial neural networks, which are a class of algorithm loosely inspired by the human brain.” — Deep Learning - Andrew W. Trask.
Although Machine Learning was a huge step in the right direction, something was still missing from its algorithms:
💡 First, the work of collecting, cleaning, and selecting the features still had to be done by hand by the developers, which involved whole days or weeks of dipping into the context of the problem to choose the best features.
💡 Secondly and most importantly, machine learning algorithms didn’t have the computational power to train themselves. Neural networks have existed since 1958 and are, part of the machine learning algorithms toolbox, however, they were single layer structures (known as perceptrons). Training a deep neural network with the hardware available at that time was impossible. Thanks to developments in GPUs and other more powerful hardware, deep networks were able to deliver results and leave their single-layer predecessors in the past.
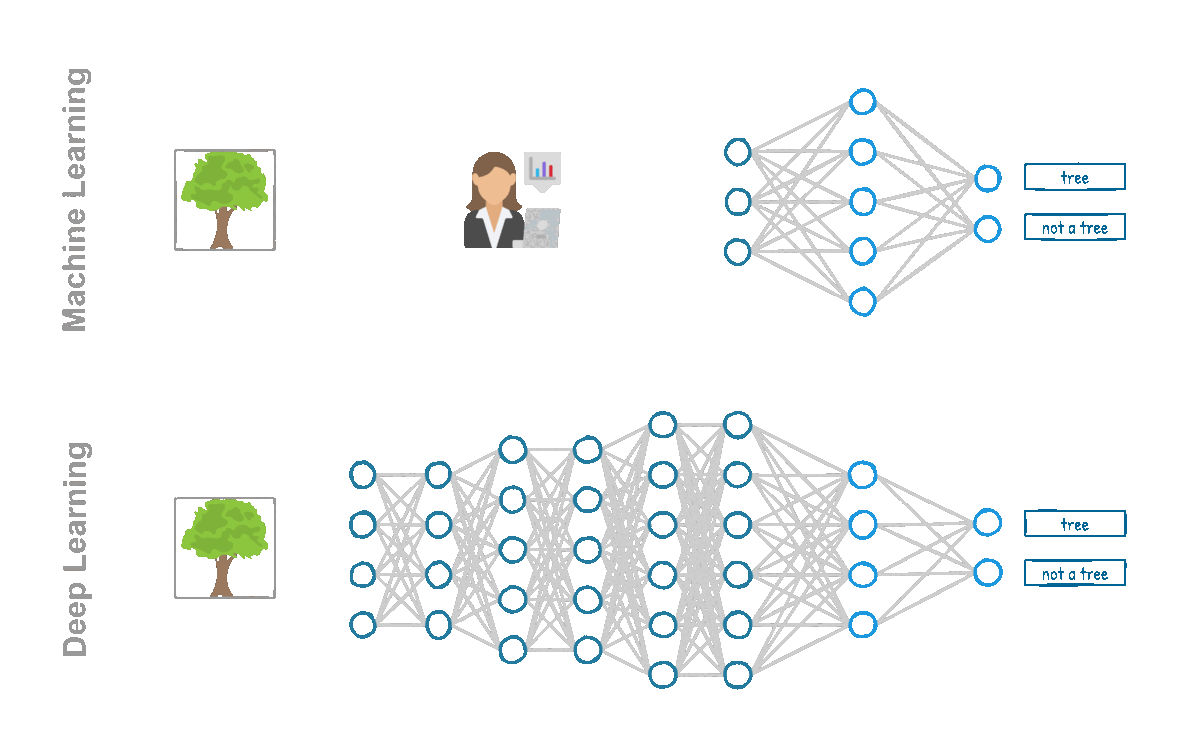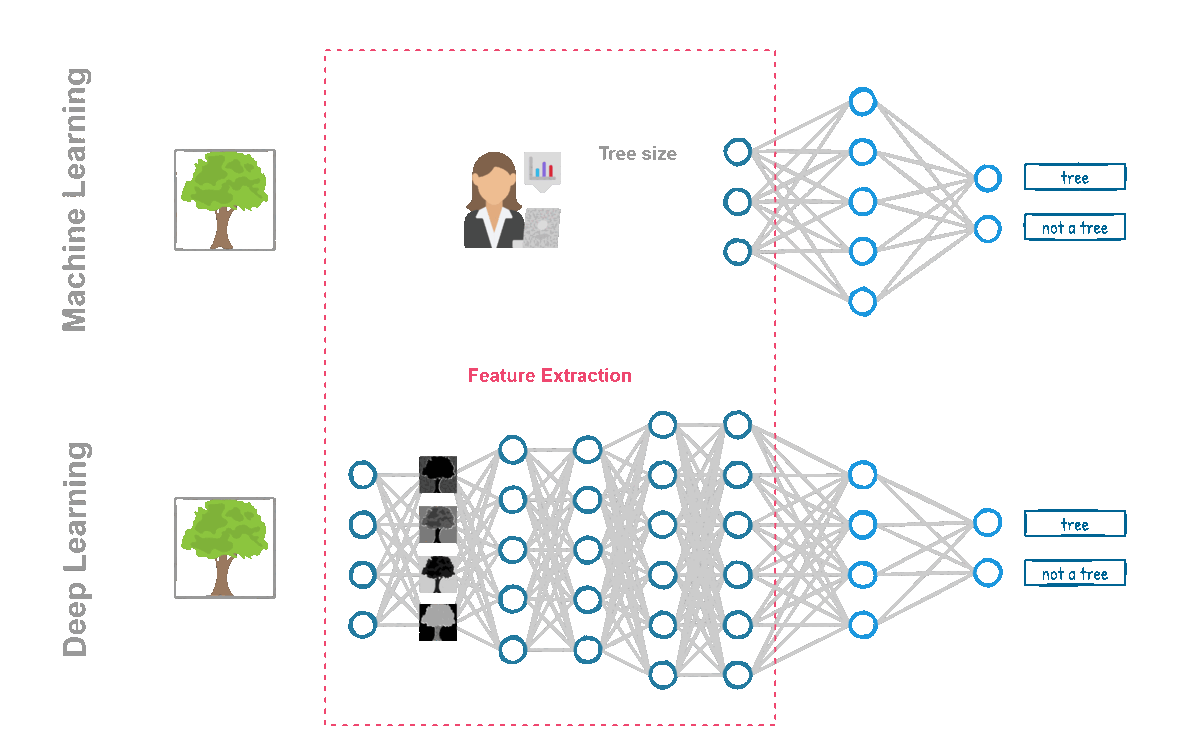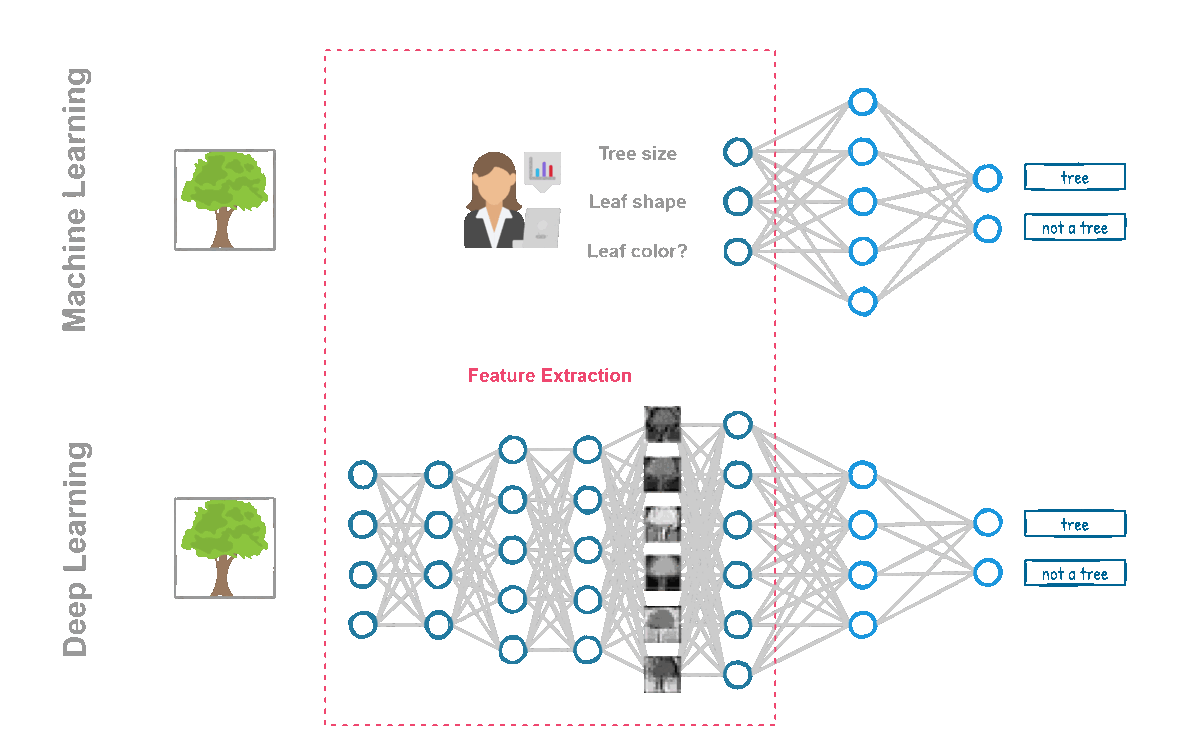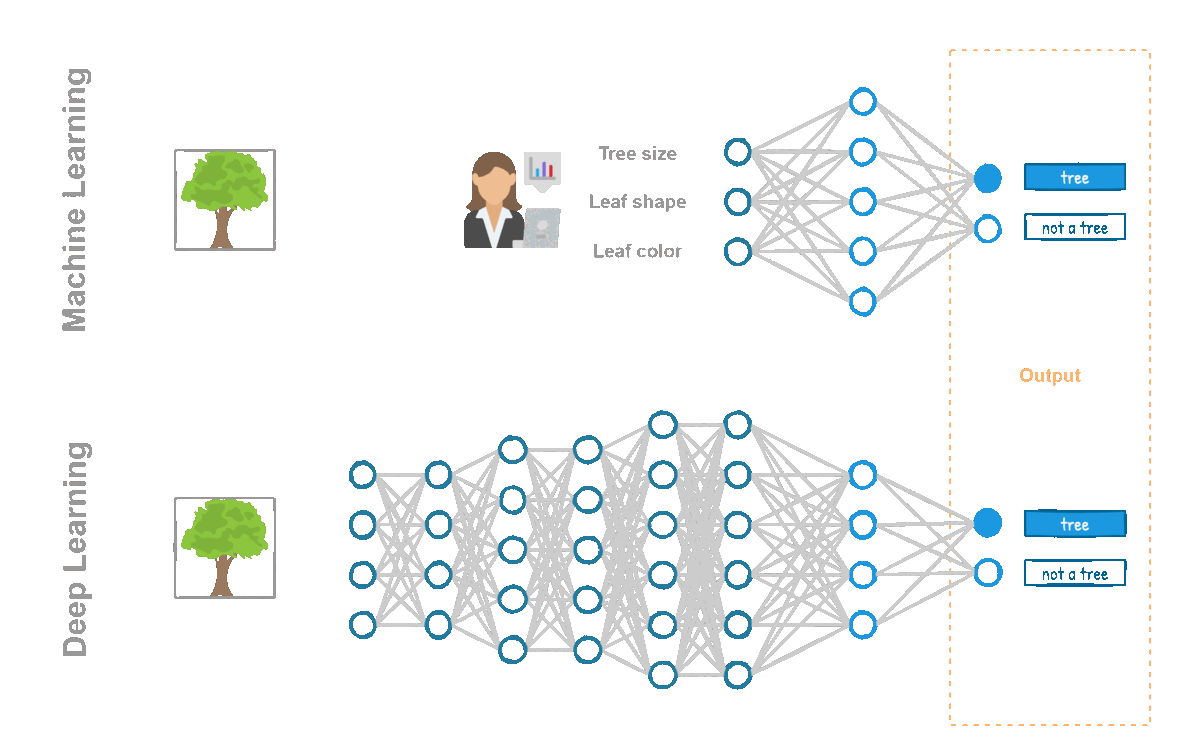
Understanding the Difference between AI, ML and DL
Some people may confuse the terms AI, ML and DL. And although they are related, they are not the same:
-
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the broader concept of machines being able to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence, such as visual perception, speech recognition, decision-making, and language translation.
-
Machine Learning (ML) is a subset of AI that involves teaching computers to learn from data, without being explicitly programmed. It involves building mathematical models that can make predictions or decisions based on input data.
-
Deep Learning (DL) is a type of machine learning that uses artificial neural networks, which are modeled after the structure of the human brain. It is called “deep” because these neural networks have many layers, allowing the computer to learn and make complex decisions. Deep learning is particularly useful for tasks such as image and speech recognition.
