What is Semi-Supervised Learning?
What is Semi-Supervised Learning?
“Since labeling data is usually time-consuming and costly, you will often have plenty of unlabeled instances, and few labeled instances. Some algorithms can deal with data that’s partially labeled. This is called semisupervised learning.” — Hands on Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras and TensorFlow - Aurélien Géron.
Semi-supervised learning is a combination of elements from both supervised and unsupervised learning. In semi-supervised learning, the computer is given a dataset that has both labeled data and unlabeled data.
Think of it like having a teacher who provides answers for some of the practice problems, but not all of them. In the same way, the computer can use the labeled data to make predictions, but must also explore the unlabeled data to find patterns and relationships on its own.
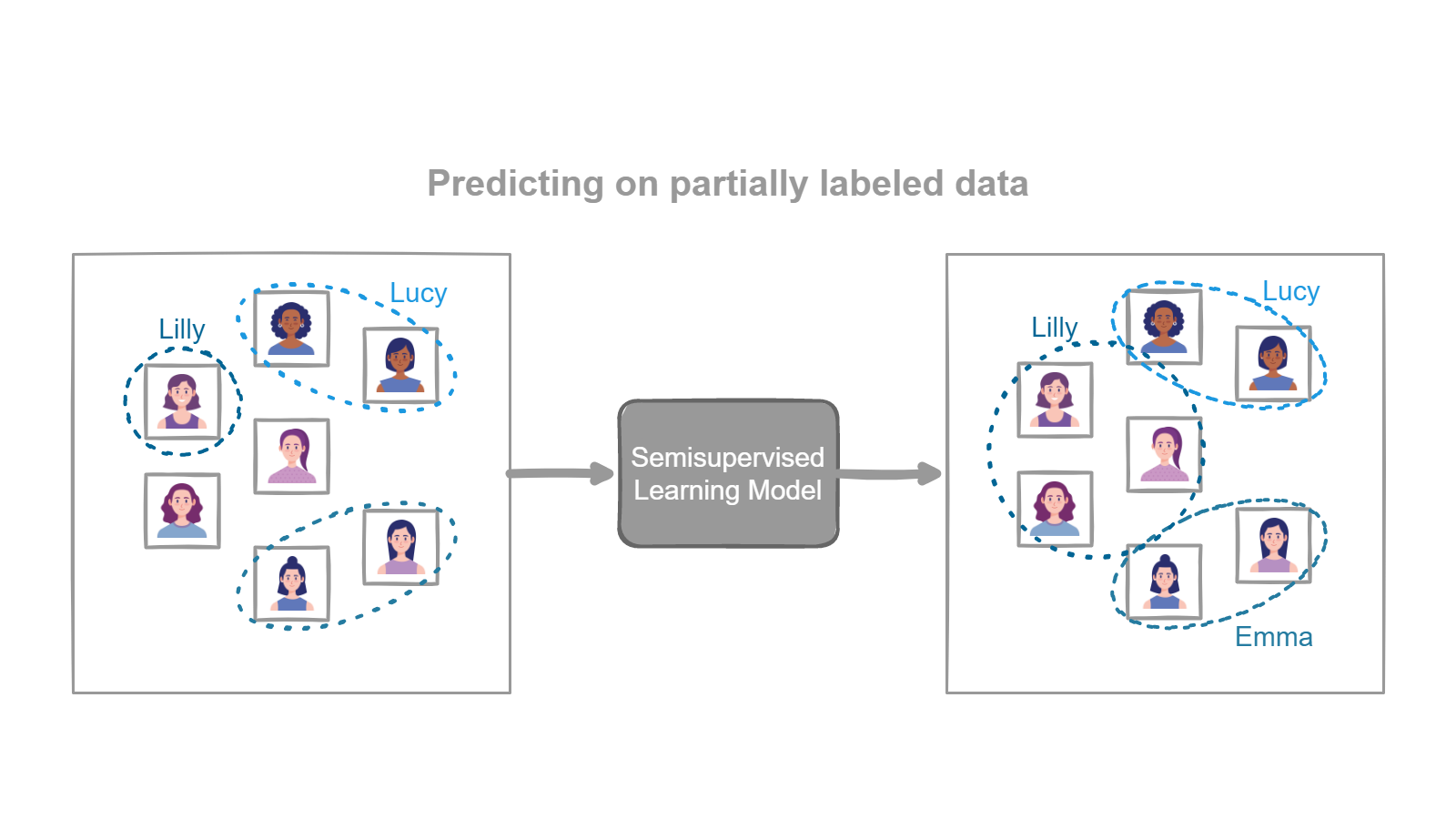
For example, a semi-supervised learning algorithm might be used to classify images into different categories. The algorithm might be given a small amount of labeled data, such as images with their corresponding labels, and a larger amount of unlabeled data, such as images without labels. The algorithm can then use the labeled data to make predictions about the unlabeled data, and can also use the patterns it finds in the unlabeled data to improve its performance.
Semi-supervised learning is useful in situations where there is limited labeled data available, or when the cost of labeling data is high. By combining the strengths of both supervised and unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning can often achieve better results than either approach alone.
Semi-supervised learning is extremely useful for problems that require Classification and Clustering.
“In semi-supervised learning, the dataset contains both labeled and unlabeled examples. Usually, the quantity of unlabeled examples is much higher than the number of labeled examples. The goal of a semi-supervised learning algorithm is the same as the goal of the supervised learning algorithm”. — The Hundred Page Machine Learning - Perter Norvig.
