How does Machine Learning Work?
How does Machine Learning Work?
Machine learning is a way for computers to learn and make decisions based on data, without being explicitly programmed.
Imagine you want to teach a computer to recognize different types of fruits. You give the computer many pictures of fruits along with their labels (e.g. apple, banana, orange).
The computer then uses this information to learn the characteristics of each fruit and build a model.
This model can then identify new fruits based on their characteristics. Just like a child learns from their experiences, the computer learns from the data it was trained on.
Over time, it can continue to improve its understanding of the fruits by learning from more and more data. This is how machine learning algorithms can become more accurate over time. Machine Learning also makes predictions.
For example, a machine learning algorithm can look at data about a person’s income, education, and age and use this information to predict their likelihood of getting a loan.
We can think of machine learning as a teacher that helps the computer learn from data and make predictions or decisions on its own.
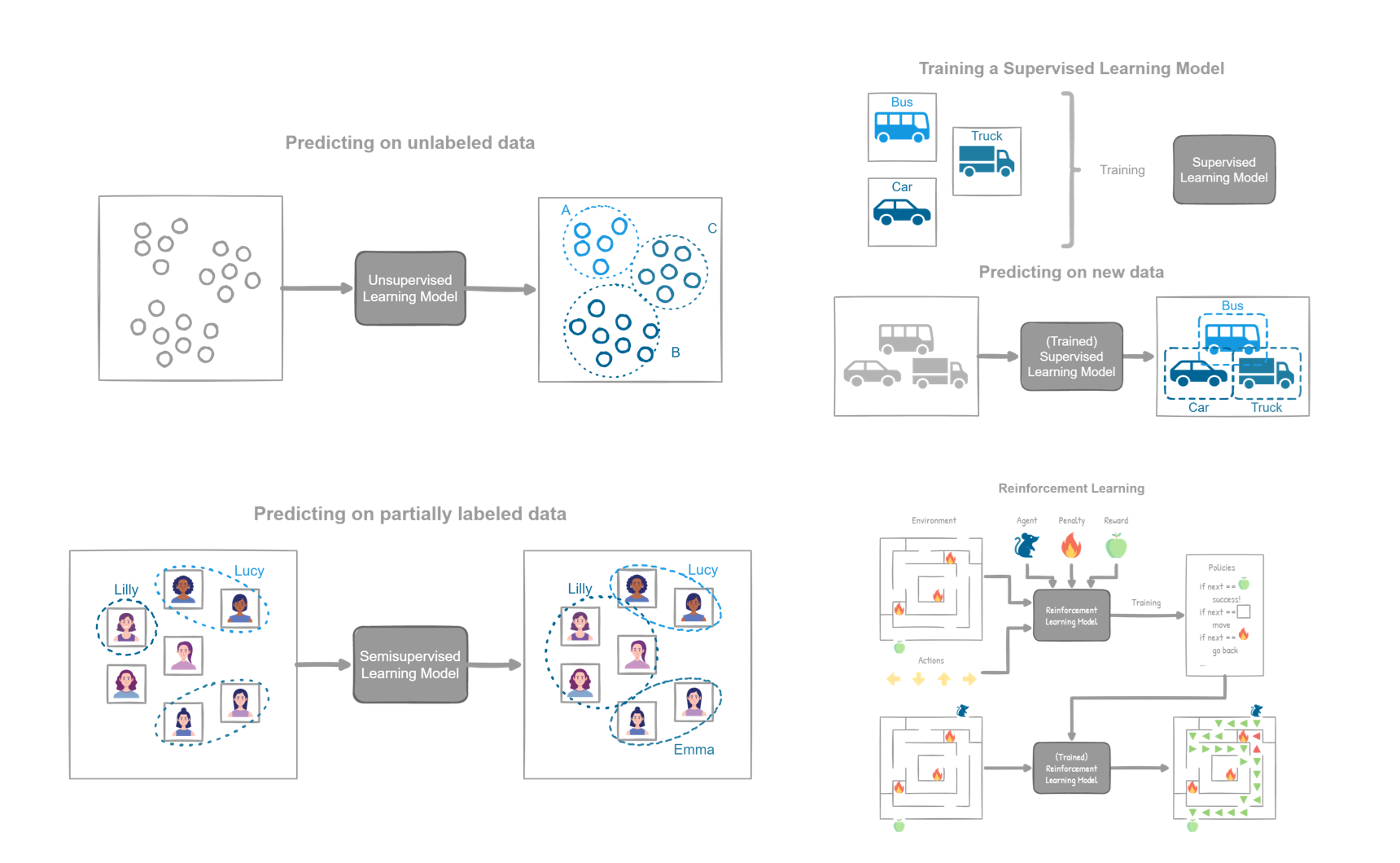
Learning Types
A system can learn in 4 different ways, depending on the data it has available to learn and the process it follows to convert the inputs into outputs:
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- Semi-supervised learning
- Reinforcement learning
Tomorrow I will tell you about the first type, supervised learning.
