Supervised Learning
Supervised Learning
“In supervised learning, the training set you feed to the algorithm includes the desired solutions, called labels”. Hands on Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras and TensorFlow - Aurélien Géron
Supervised learning is a type of machine learning in which the computer is given a set of labeled data and uses that data to make predictions about new, unseen data.
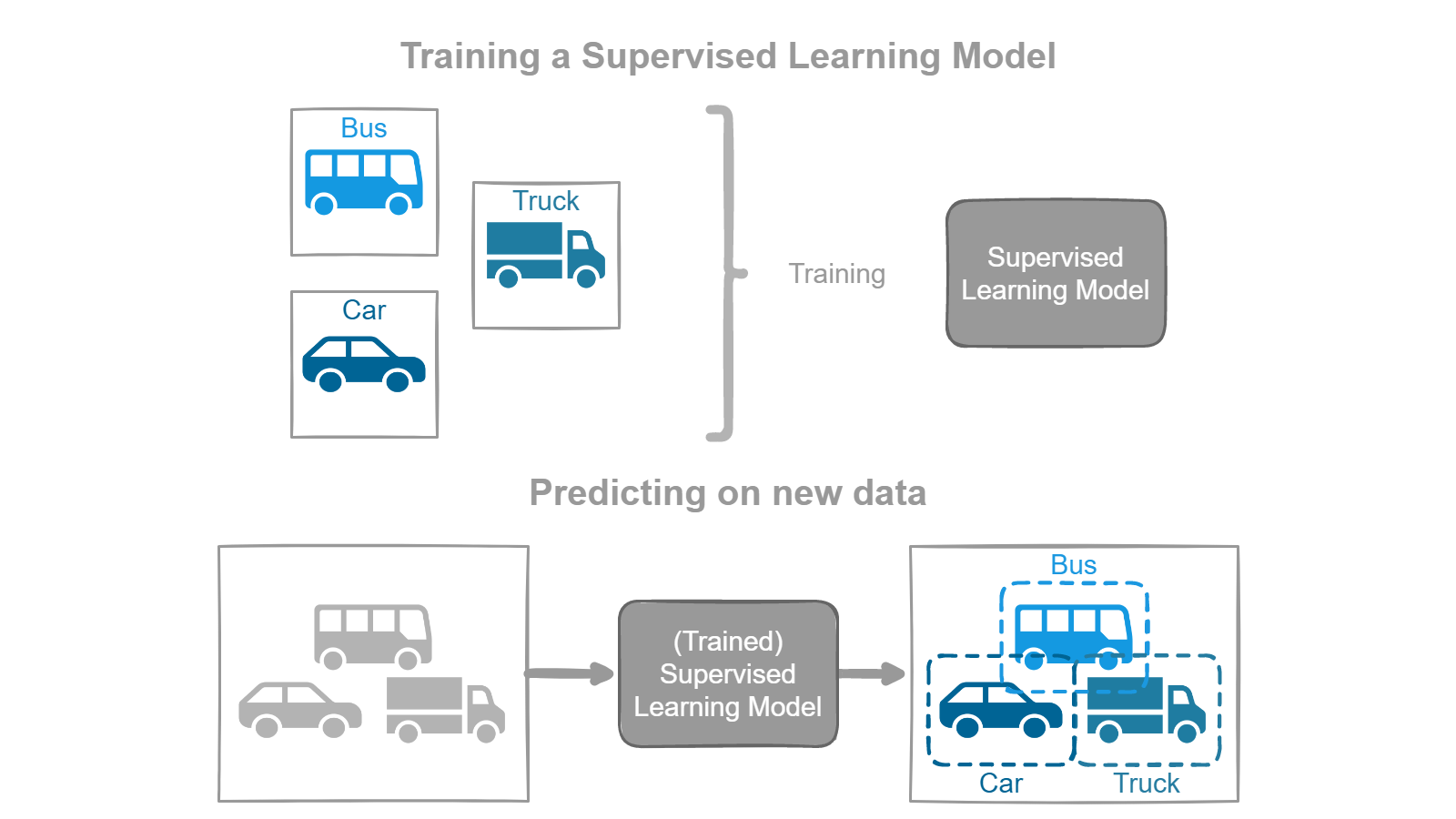
Think of it like a teacher giving a student practice problems to solve. The teacher provides the student with the answers (the labeled data), and the student uses that information to solve new problems (the unseen data). In the same way, the computer uses the labeled data to make predictions about the new data.
For example, a supervised learning algorithm might be trained on a dataset of pictures of animals and the labels that tell the algorithm what type of animal is in each picture. Once the algorithm has been trained, it can then be used to make predictions about new pictures of animals that it has never seen before.
“The goal of a supervised learning algorithm is to use the dataset to produce a model that takes a feature vector x as input and outputs information that allows deducing the label for this feature vector”. — The Hundred Page Machine Learning - Perter Norvig.
Some of the most popular problems solved with Supervised Learning are Regression, Classification, Detection, Forecasting, Ensembling, Recommendation, Ranking, and Anomaly Detection.
Supervised learning is a powerful tool for solving many real-world problems, such as image classification, spam filtering, and predictive maintenance. The key to success with supervised learning is having a large and diverse dataset to train the algorithm on, as well as carefully designing the algorithm itself to make the best predictions possible.
Tomorrow I’ll tell you about the next type of learning.
